Topographic Maps are helpful because they show land features and terrain.
Features
A topographic map shows the following features;
- cultural - roads, buildings, urban development, railways, airports, names of places and geographic features.
- hydrography - lakes, rivers, streams, swamps and tidal flats.
- relief - mountains, valleys, slopes and depressions.
- vegetation - wooded and cleared areas, vineyards and orchards.
 Before the features from the Earth's curved surface can be shown on a flat map, the position of a constant point is needed. This fixed point is called a geodetic datum and for New Zealand is based on the Earth's centre of mass.
Before the features from the Earth's curved surface can be shown on a flat map, the position of a constant point is needed. This fixed point is called a geodetic datum and for New Zealand is based on the Earth's centre of mass.
Scale
The level of detail shown on maps depends on the scale of the map. A small scale map shows less detail than a larger scale map.
In New Zealand topographic maps are made by Land Information New Zealand (LINZ). These maps are at a scale of 1:50,000 which means one centimetre on the map represents 50,000 centimetres, or 500 metres on the ground. These maps are known as Topo50 maps.
LINZ also produces smaller scale maps which are useful for planning travel over large distances, or for giving an overview of New Zealand. You can see the different map scales in the table below.
Examples of map scales;
| Scale | Ground distance of 1cm on the map |
| 1:50,000 | 500 metres (NZ Topo50 maps) |
| 1:250,000 | 2.5 kilometres |
| 1:1 million | 10 kilometres |
| 1:2 million | 20 kilometres |
Who Uses Topo50 maps
Topo50 maps show geographic features in detail. They are useful for a wide range of activities, such as;
- local navigation by vehicle or on foot
- search and rescue and emergency services
- environmental studies
- planning and development
- outdoor activities for example tramping, climbing, hunting, caving, cycling, orienteering.
Direction
Topographic maps include a north point in the map margin information. This shows the direction of Grid North and Magnetic North and is used to orient the map.
Legend
The legend on a map shows the symbols used to represent features on the ground. These features include roads, tracks, rivers, lakes, vegetation, fences, buildings, power lines etc. Given the size of the map it is not possible to show all features on the ground. Symbols are grouped in themes on the legend.
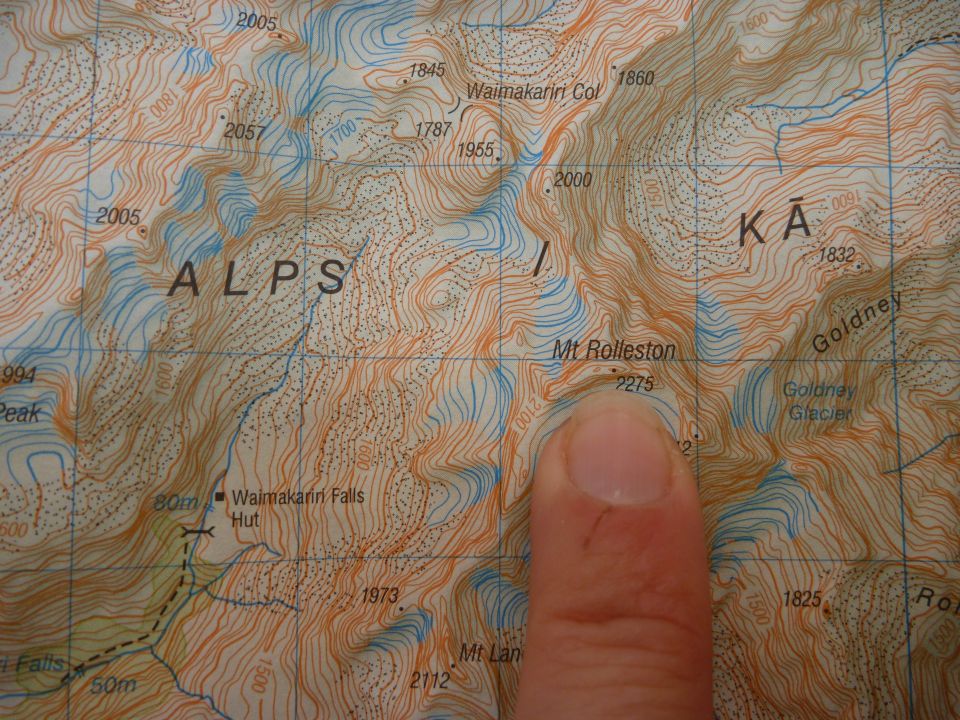
Contour lines
Topo50 maps show 20 metre contour lines. These lines join points of equal height and represent the relief or height of the land. Contour lines that are close together show steep land. Contour lines that are far apart show that the land has gentle slopes.
As well as contour lines, maps also show relief shading to help visualise the terrain. Hills and valleys are shaded as if the sun was shining from the north-west.
Coordinates
Map coordinates can be shown as:
- Geographical coordinates, given as latitude and longitude values in degrees, minutes and seconds e.g. Christchurch Cathedral = 43.5309° S, 172.6370° E.
- Grid coordinates, given as easting and northing values, in metres for example coordinates for the Christchurch Cathedral = 2480635,5741760.
To find out more about reading topographical maps go to the 36 page LINZ Topo50 Map guide (PDF 1.5Mb).
Visit the online topographic maps at http://www.topomap.co.nz/.
Access to digital map data that LINZ uses to make printed topographic maps is available through the online LINZ data service LDS.








Comments
I wonder if trampers still prefer printed topo maps