You can contact LEARNZ, part of CORE Education, at:
Postal Address:
PO Box 13 678,
Christchurch 8141,
New Zealand
Landslides are a natural process that removes material from hills, mountains and coastlines. Landslides are common in New Zealand and can range from small events to damaging large scale events.
Compared to many other countries, New Zealand has a high number of landslides because:
Some landslides move whole mountain sides, taking millions of cubic metres of material, at up to 200 kilometres per hour. Others are shallow or slow, moving only a few centimetres a year.
On unstable slopes, three things are important in producing large landslides:
Deforestation has had the largest impact on the stability of hillsides. Clearing land for farming has increased landslide activity by about seven times its natural rate. Road construction and subdivision earthworks can also destabilise slopes and increase landslide rates.
There are different types of landslides, these include:
Each year local councils, roading authorities, private landowners and railway operators spend millions of dollars clearing slips from roads and railway lines. It is a never-ending task – there are always more floods or earthquakes to come, and there is plenty of rock and soil waiting to tumble down.
In general, landslides are more common in New Zealand than many countries because of the terrain and less stable conditions. However, landslides cause few deaths in New Zealand because there are few settlements in mountainous areas and the population density is relatively low.
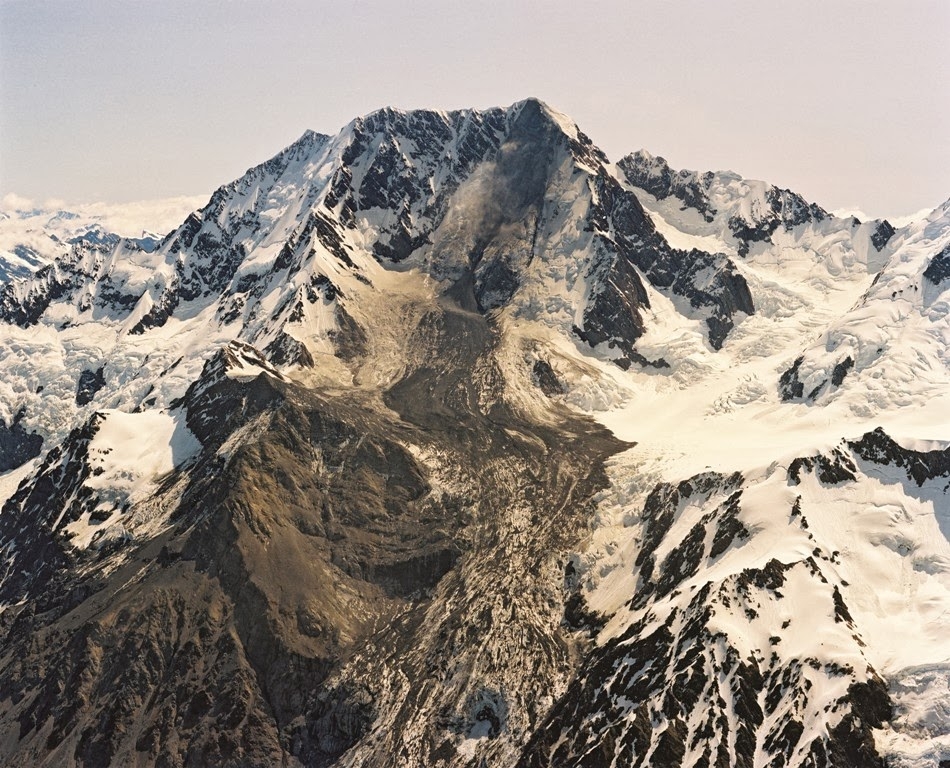

,A massive rock avalanche changed the height of New Zealand's highest mountain, Aoraki Mount Cook, in December 1991. Can you find out about other large rock avalanches in New Zealand? Image: Loyd Homer, GNS Science.

,Landslides are common in New Zealand. This landslide is in Whakatāne. Can you find out what large landslides there have been in New Zealand recently. Image: LEARNZ.

,One of New Zealand's most well known landslides was the 1979 Abbotsford landslide in Dunedin which left 69 houses uninhabitable. What type of landslide was this and was anyone hurt? Image: GNS Science.
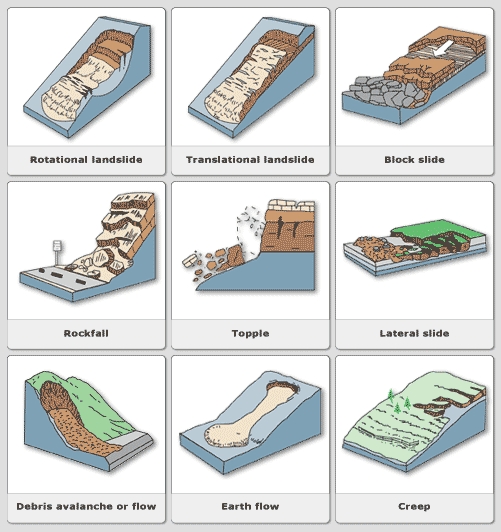
There are different types of landslides. Sometimes landslides can be a combination of different types. What are the most common landslides in New Zealand? Image: United States Geological Survey. Art work by Margot Johnson.
You could find out if and where there has been a landslide in your local area and what caused it.