You can contact LEARNZ, part of CORE Education, at:
Postal Address:
PO Box 13 678,
Christchurch 8141,
New Zealand
Kiwi are well adapted to life on the ground.
A male kiwi needs a territory before he can attract a mate. They will fight to protect their territory. Once territories are found, kiwi call to mark the edge of their territory.

Kiwi usually stay together as a life-long couple. The female is bigger and dominates the male.
A burrow can take many forms, depending on the species and the location.
The burrow is usually lined with soft leaves, grass and moss. When inside, kiwi often pull leaves and sticks across the entrance as camouflage and to keep in heat and moisture.
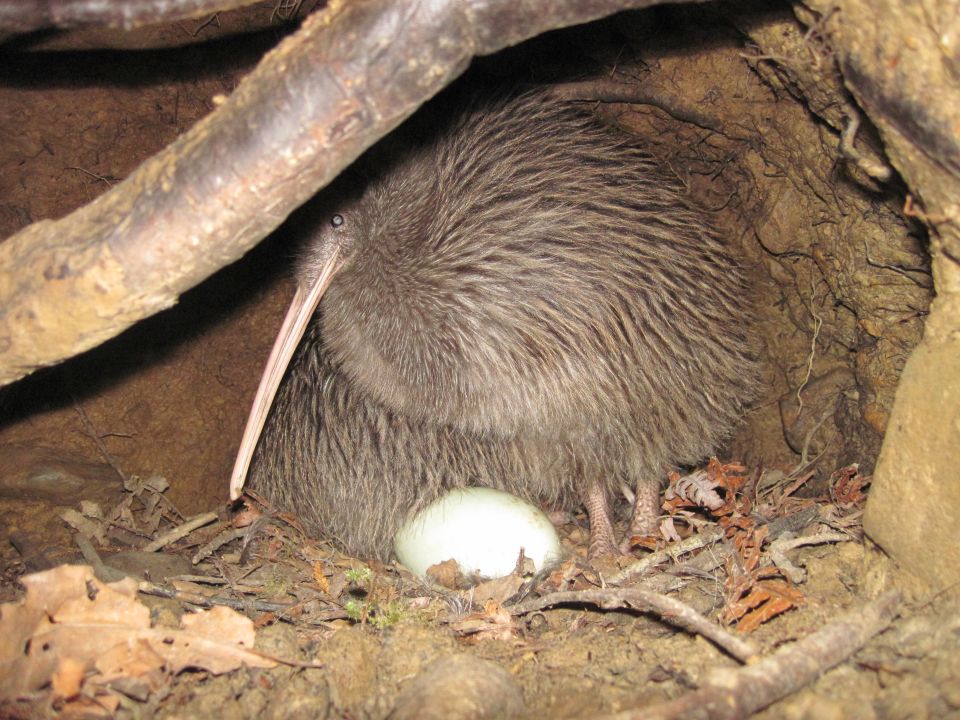

The main breeding season runs from June to March, when there is a lot of food around. Brown kiwi in the North Island can lay eggs in any month. Wild females lay their first eggs at 3-5 years of age.
Kiwi eggs are one of the largest eggs in the world - six times larger than birds of the same size or weight.
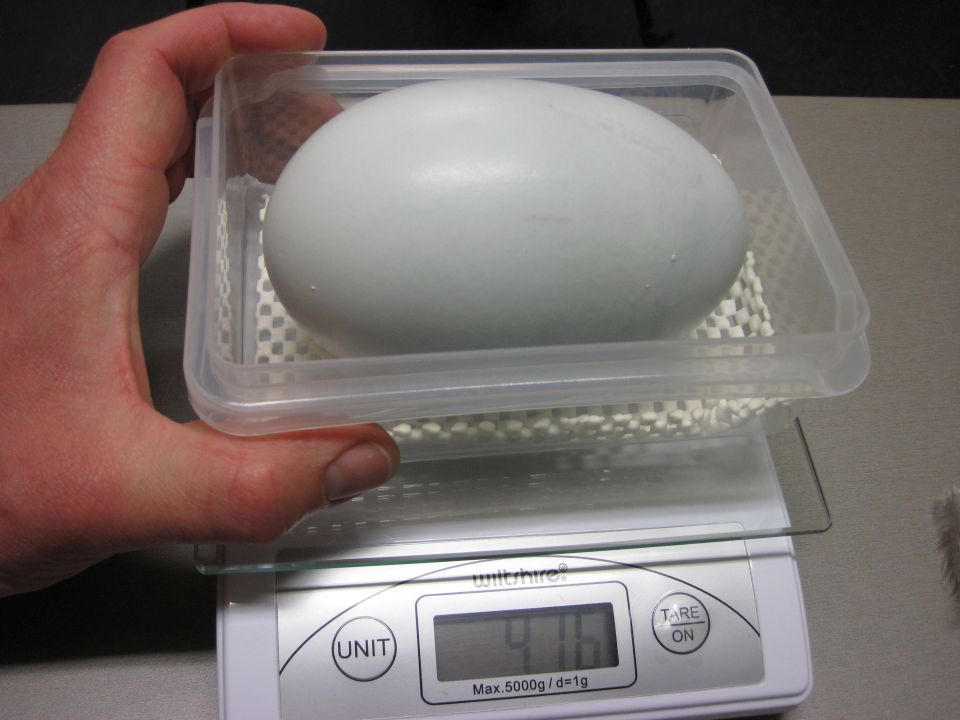

Most clutch sizes are one egg. Brown kiwi usually lay two eggs in a clutch. The egg is laid quickly and is incubated for 70-80 days. The eggs are incubated just by the male parent in the little spotted and brown kiwi species. Both parents in the great spotted, rowi and tokoeka kiwi share incubation.
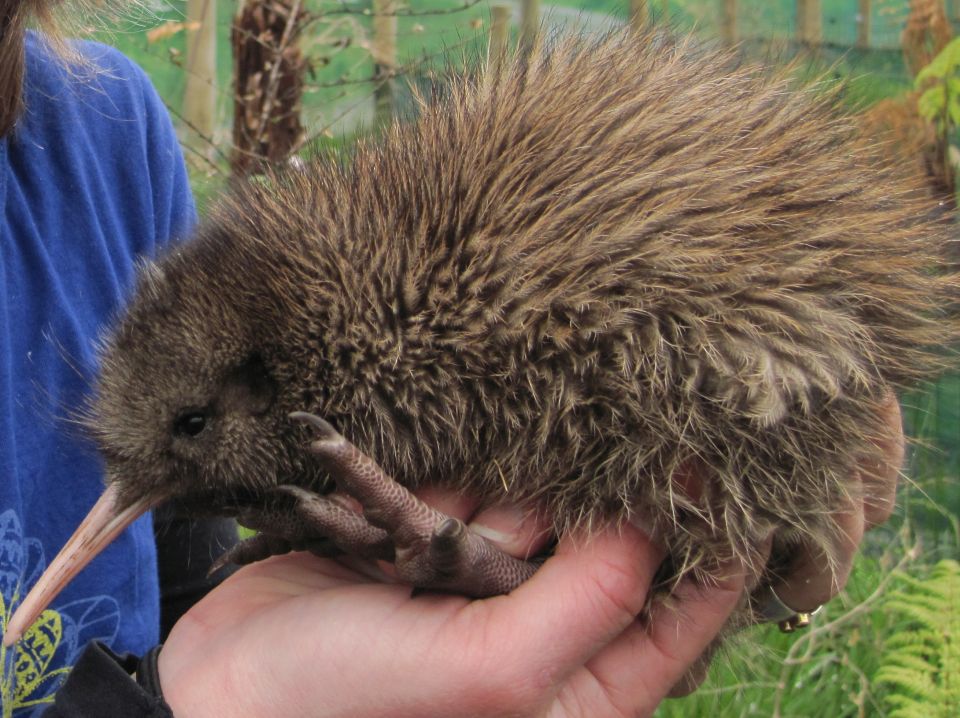
It can take up to three days for a kiwi to hatch. Kiwi chicks hatch as mini-adults – fully feathered and open-eyed. Their beaks are soft and pink. Kiwi chicks hatch with a large external yolk sac, which means they do not have to go outside to feed for the first few days.
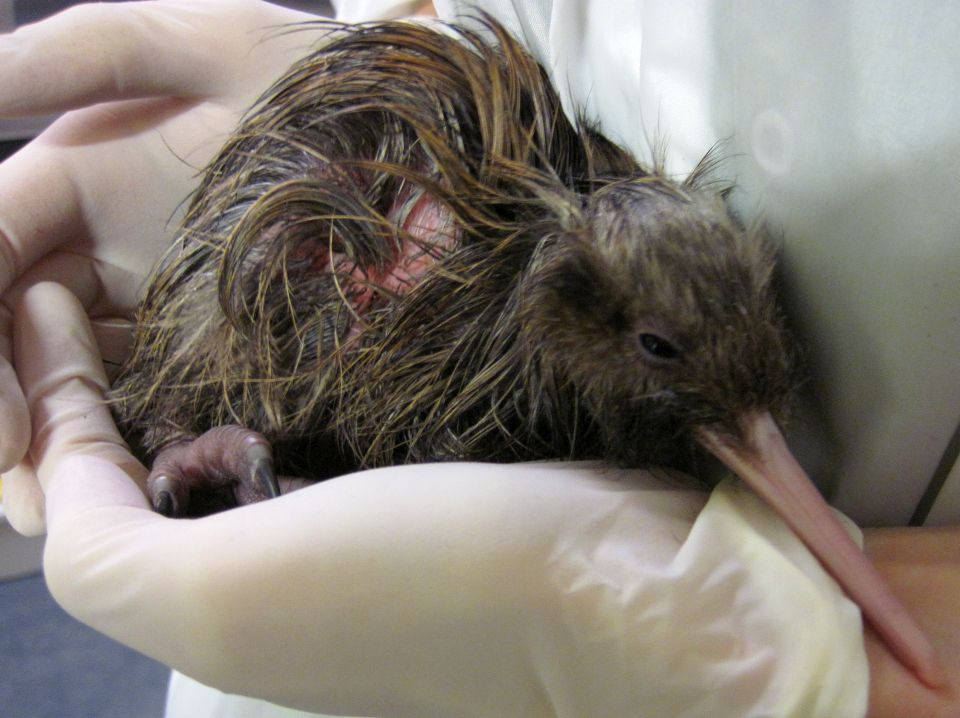
During its first three-to-four weeks, the baby kiwi feeds at night, and sometimes during the day. This makes it very exposed to predators. Only about 5% of kiwi chicks born in the wild survive to adulthood.
Young kiwi grow slowly until they are about four years old. Some brown kiwi leave their parents’ territory when they are four-to-six weeks old. Young great spotted kiwi stay in their parents' territory for a year or more. Stewart Island tokoeka and rowi can remain with their parents for up to seven years, helping raise their siblings.

Kiwi can live as long as 50 to 60 years.