<- Homepage: Kiwi: from lifted egg to free adult

New Zealand Curriculum (NZC)
This field trip supports a cross-curricular approach to teaching and learning. It is guided by the 2007 New Zealand Curriculum. It aligns best with, but is not limited to, the learning areas, year groups and progressions presented below.
Select one or more learning areas, concepts and progress outcomes to suit your students’ interests and learning needs.
Use this learning experience as a springboard for multiple areas of inquiry. Look for ways to make connections to learning that matters to students, as well as nationally and locally.
Science (NZC 2007)
Nature of science
The nature of science strand is the overarching, unifying strand. Through it, students learn what science is and how scientists work. They develop the skills, attitudes, and values to build a foundation for understanding the world. They come to appreciate that while scientific knowledge is durable, it is also constantly re-evaluated in the light of new evidence. They learn how scientists carry out investigations, and they come to see science as a socially valuable knowledge system. They learn how science ideas are communicated and to make links between scientific knowledge and everyday decisions and actions. These outcomes are pursued through the following major contexts in which scientific knowledge has developed and continues to develop.
- Participating and contributing
Levels 1-2: Explore and act on issues and questions that link their science learning to their daily living.
Levels 3-4: Use their growing science knowledge when considering issues of concern to them. - Investigating in science
Levels 1-2: Extend their experiences and personal explanations of the natural worl through exploration, play, asking questions, and discussing simple models.
Levels 3-4: Ask questions, find evidence, explore simple models, and carry out appropriate investigations to develop simple explanations.
Living world
The living world strand is about living things and how they interact with each other and the environment. Students develop an understanding of the diversity of life and life processes, of where and how life has evolved, of evolution as the link between life processes and ecology, and of the impact of humans on all forms of life. As a result, they are able to make more informed decisions about significant biological issues. The emphasis is on the biology of New Zealand, including the sustainability of New Zealand’s unique fauna and flora and distinctive ecosystems.
- Ecology
Levels 1-2: Recognise that living things are suited to their particular habitat.
Levels 3-4: Explain how living things are suited to their particular habitat and how they respond to environmental changes, both natural and human-induced. - Life processes
Levels 1-2: Recognise that all living things have certain requirements so they can stay alive.
Levels 3-4: Recognise that there are life processes common to all living things and that these occur in different ways.
Te ao tangata | Refreshed social sciences learning area
Progress outcome by the end of year 8:
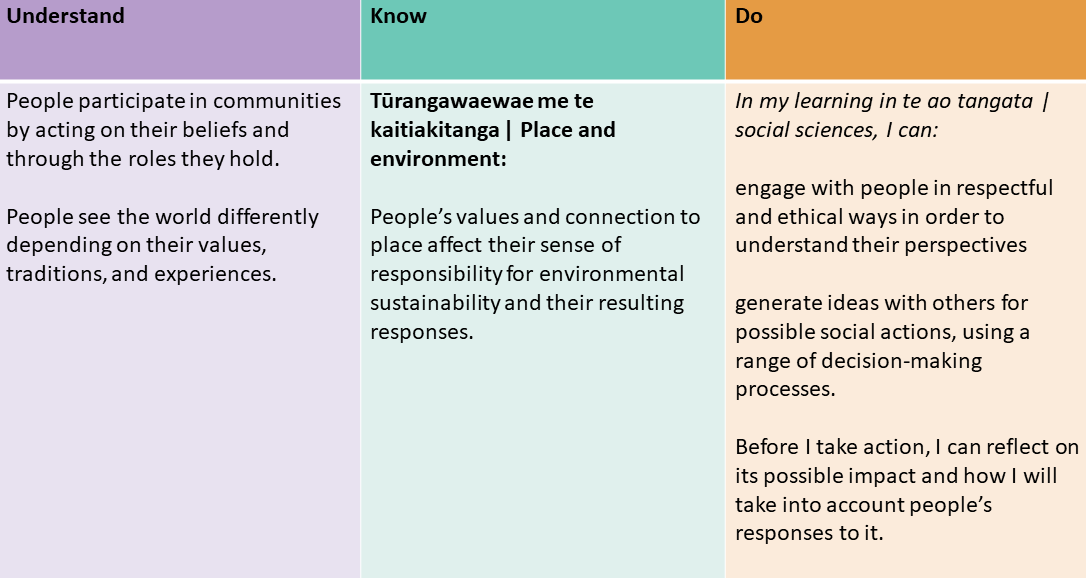
Inquiry practice that brings rigour to learning:
Key questions:
- What is the role that native birds have in our rohe?
- Which native bird species are at risk and what are the implications for our community?
Learning experiences:
- Explore native bird species in our rohe and how different people in our community value them.
- Explore the reasons why our native bird species face challenges and threats.
- Explore the different ways in which we value and connect with the land, its flora and fauna, and how our actions can create negative and positive impact.
Social sciences continued (NZC 2007)
The social sciences learning area is about how societies work and how people can participate as critical, active, informed, and responsible citizens. Contexts are drawn from the past, present, and future and from places within and beyond New Zealand.
- Place and environment
Level 1: Understand how places in New Zealand are significant for individuals and groups.
Level 2: Understand how places influence people and people influence places.
Level 3: Understand how groups make and implement rules | Understand how people view and use places differently.
Level 4: Understand that events have causes and effects.
English (NZC 2007)
Listening, reading and viewing
Ideas: Show a developing understanding of ideas within, across, and beyond texts.
E.g. Indicators at level 3:
- uses their personal experience and world and literacy knowledge confidently to make meaning from texts
- makes meaning of increasingly complex texts by identifying main and subsidiary ideas in them
- starts to make connections by thinking about underlying ideas in and between texts
- recognises that there may be more than one reading available within a text
- makes and supports inferences from texts with increasing independence.



