Who has heard of GPS?
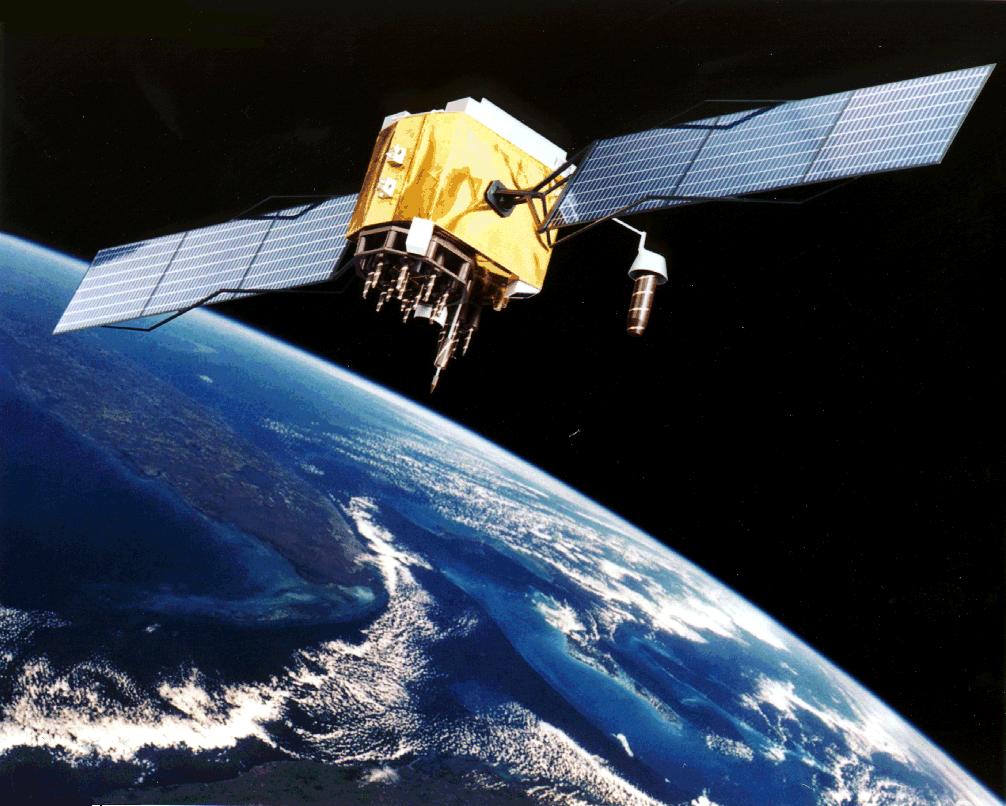
GPS Stands for Global Positioning System and they are now used throughout the world. A GPS unit is actually a receiver that collects signals from satellites.
Global Positioning System satellites transmit signals to GPS receivers on the ground. Receivers require a clear view of the sky, so they are used only outdoors and do not perform well in forests or near tall buildings.

Each GPS satellite has an atomic clock and sends a signal stating its location and the exact time. All GPS satellites transmit at the same instant. The signals move at the speed of light and arrive at a GPS receiver at slightly different times because some satellites are further away than others. The distance to the GPS satellites can be calculated by estimating the amount of time it takes for their signals to reach the receiver. When the receiver estimates the distance to at least four GPS satellites, it can calculate its position in latitude, longitude and height.
How GPS Works
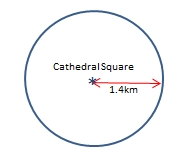
Imagine you are somewhere in Canterbury and you are totally lost. You have absolutely no clue where you are. You find a friendly local and ask, "Where am I?" he says, "You are 1.4km from Christchurch’s Cathedral Square”.
That is good hard evidence but it means you could be anywhere on a 9km circle around Cathedral Square.
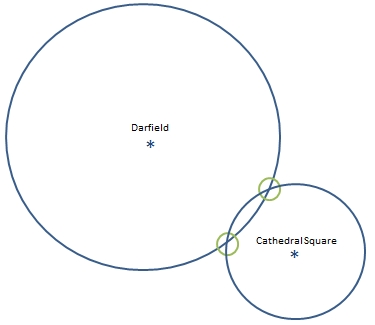
You ask someone else where you are and she says “you are 5.3km from Darfield”.
Now you're getting somewhere. If you combine this information with the Cathedral Square information, you have two circles that intersect. You now know that you must be at one of these two intersection points, if you are 1.4km from Cathedral Square and 5.3km from Darfield.
A third person tells you that you are 3.2km from Rangiora.
You can now eliminate one of the possibilities, because the third circle will only intersect with one of these points. You now know exactly where you are: Christchurch International Airport.
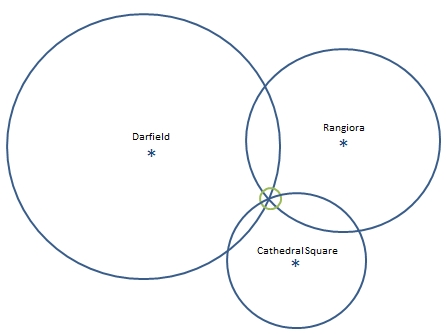
Each of the three circles represents the signals received from GPS satellites. The main difference is that rather than measuring to three known locations on the surface of the Earth, you are measuring to the known location of three GPS satellites.
A fourth signal is used to synchronize the low accuracy clock in the GPS receiver with the high accuracy atomic clocks in the satellites.
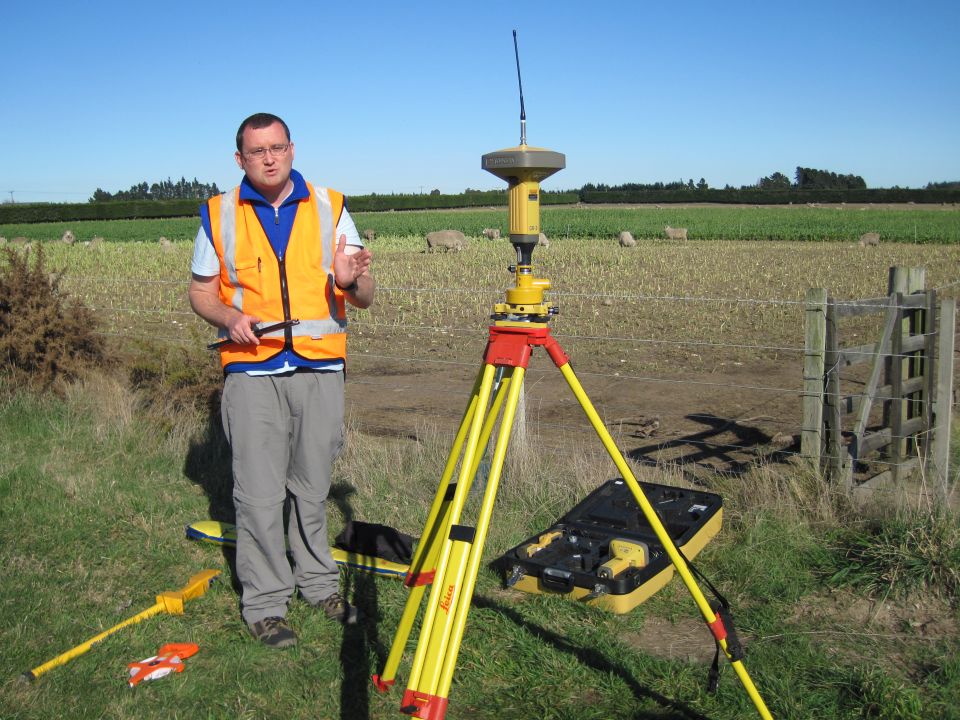
To get the best accuracy, surveyors use two GPS receivers to measure the distance between two points. One of the GPS receivers is set up on a point with a known position. This allows the surveyor to calculate the position of the second point.
Uses of GPS
GPS has many uses, for example;
- Clock synchronization: The GPS time signals use highly accurate atomic clocks. This technology can be used for things like automatic updates of daylight saving times on cell phones.
- Disaster relief and emergency services: Depend upon GPS for location.
- Tracking a vehicle, person, pet or aircraft: Receivers provide continuous tracking and can provide an alert if the receiver leaves a set area. Pets can be chipped so they can be found if they become lost.
- Navigation: eg Navman. The device uses voice activation to describe a preferred route based on the position of the receiver, the position of the destination and a street map.
There are many other uses for GPS: can you think of more examples?







