What is climate change?
Climate change is the change in weather patterns that we can see on earth over long periods e.g. hundreds to millions of years. Climate can change naturally because of changes in:
- volcanic eruptions
- ocean currents
- solar radiation
How is weather different from climate?
Human induced changes
People have caused recent changes in climate by increasing the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases cause global warming by preventing heat from escaping back into space.
What evidence do scientists use to show that current climate change has been caused by people and how do we know this evidence is accurate?
What are greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases are those that help cause the 'greenhouse effect'. Without greenhouse gases the earth would be very, very cold (about 30° colder). Greenhouse gases include:
- water vapour
- carbon dioxide
- methane
- nitrous oxide
- ozone
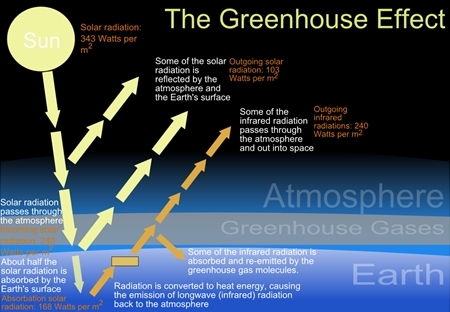
What is the ‘greenhouse effect’?
The ‘greenhouse effect’ is what happens when the sun’s radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases, and is re-radiated back towards the earth. This results in a rise of the surface temperature; A bit like in a greenhouse.
One of the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide, has been increasing rapidly since the beginning of the industrial revolution (1750) when humans started burning greater amounts of fossil fuels (such as coal and oil).
 Before 1750 (the start of the industrial revolution) the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere was about 270 parts per million (ppm). The concentration has increased to nearly 400 ppm in 2012. The graph below is sometimes called the Keeling Curve after Charles David Keeling who was the first person to measure this increase.
Before 1750 (the start of the industrial revolution) the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere was about 270 parts per million (ppm). The concentration has increased to nearly 400 ppm in 2012. The graph below is sometimes called the Keeling Curve after Charles David Keeling who was the first person to measure this increase.
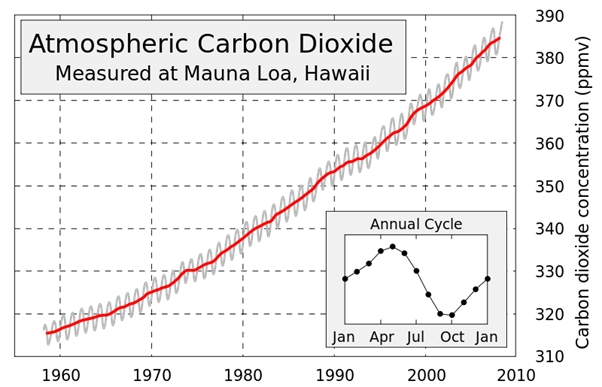
This increase in CO2 causes the man-made portion of the greenhouse effect that has caused global warming.
Why is this a useful way of displaying data about carbon dioxide concentrations and why do you think there is such a strong annual cycle?